Cerebral Haemodynamics
Among the reasons producing neurootological diseases prevail the vascular affections. Therefore, we have introduced non-invading methods in the daily routine, in order to be able to study cerebral haemodynamics.

Sonotechnik equipment for transcranial and extracranial USD
Researching methods
We study cerebral haemodynamics by means of Ultrasound Doppler Sonography - USD, which consists in supporting a probe on the skull area, capable of giving out a sound in a frequency ( variable depending on the depth artery).
The sound is reflected by the bloodcells column which circulates through the artery, allowing the evaluation of different arterial parameters by means of computer methods:
- speed
- flow
- direction of the blood current
- peripherical resistance
- stenoses degree (occlusions)
According to the depth of the cerebral arteries to be studied, the Ultrasound Doppler Sonography could be directed towards arteries out of the skull
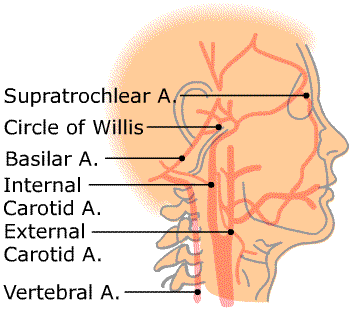

Anatomy of vertebral arteries
52% of our patients consult on vertigo based on a previous diagnosis derived from cervical disorders. The ability of measuring cerebral haemodynamics enables us to observe that