Migraines – Headache
The vascular system and its influence under stimuli of the autonomic or neurovegetative nervous system play an extremely important role, not only in Neurootology, but also in the origin of severe headache or migraine.
Every modification in capillary diameter produces nourishment disorders at cell level modifying its functions. Changes in capillary diameter could be the result of vessels dilation phenomena as it takes place in hypotensions, or of vessels spasms as it should be the case of blood hypertension.
From our Data Bank analysis, it becomes evident that 57,89% of neurootological patients present haemodynamical alterations in capillaries, 29,57% corresponding to hypertension phenomena or spasticity and 28,32% to hypotension phenomena or capillary dilations.
On top of this, 42% of patients consult on severe headaches, migraine or cephaleas, associate or not to other neurootological symptoms.
On those patients showing migraine or severe headaches the study on cerebral haemodynamics is strictly applied by means of USD-Transcranial and of the USD-Extracranial,thus issuing a diagnosis on the sort and features of cerebral vascular disorders.
As per the results obtained through studies on cerebral haemodynamics, it has been found that our patients suffer from:
| % | Headache or Migraine |
|---|---|
| 53.20% | Vasospastic form |
| 29.80% | Vasodilatic form |
| 9.09% | Combined |
| 7.70% | Without haemodynamic variations |
On patients below 40 years old, there is an equal distribution between vasospastic and vasodilatic forms, whilst on patients over 60 years old vasospastic forms prevail in 80% of the studies.
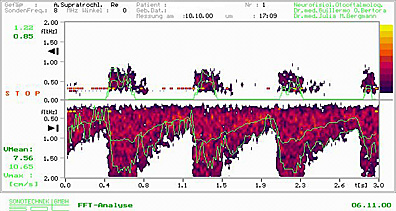
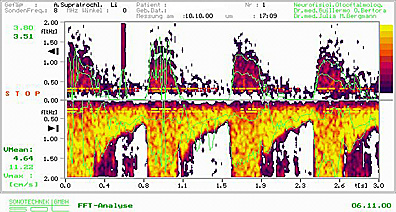
61 years old patient suffering from migraine prevailing on the left. Extracranial USD of right supratrochlear artery is within regular range, the left supratrochlear artery shows an acceleration of the flow with an increase of the stenosis index and turbidity. Typical example of vasomotorial migraine towards spastic form.
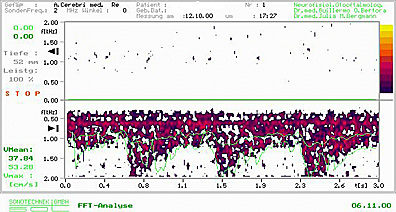
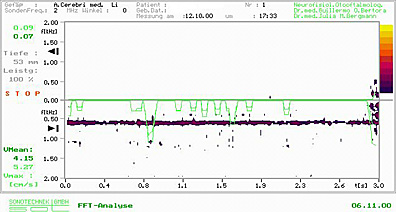
58 years old patient with diffuse headache, cognitive disorders with several months of evolution. Transcranial USD of middle cerebral arteries denotes a severe hypoflow of the middle left cerebral artery.
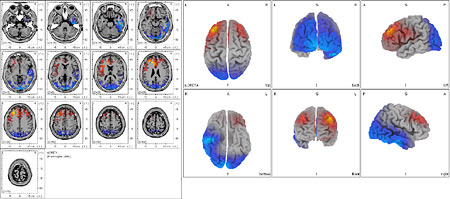
22 year old patient suffering from vasomotor migraine under dilatational form. In the Brain Electric Tomography it is observed in yellow/red a hyperactivity focus in frontal lobe and limbic left , in blue hypoactivity brain areas. This is a typical depolarization process which could be objectified in headache and migraine situations.
With the vascular changes typical of headaches and migraines, depolarization or irritation areas are produced at cerebral level which should be evaluated to solve this pathology in a global way.
Migraine treatment should be:
-
Symptomatological
Directed to counteract sharp pain symptoms. -
Etiopathogenetic
Directed to the type of vascular or neuronal affection. -
Prophylactic
Which also makes it possible to establish a preventive therapy in order to prevent future irreversible cerebral damages, as it happens in cerebrovascular diseases.